Equilibrium Quantity And Equilibrium Price Calculator

In the realm of economics, understanding the dynamics of supply and demand is crucial for analyzing market behavior. At the heart of this analysis lies the concept of equilibrium, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, resulting in a stable market price. To facilitate this understanding, economists and analysts often employ tools such as the equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price calculator. This tool enables users to determine the point at which supply and demand intersect, providing valuable insights into market dynamics.
Understanding Market Equilibrium
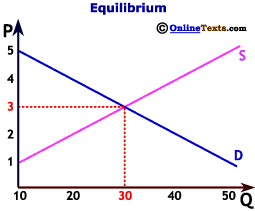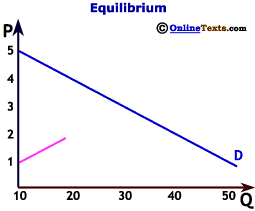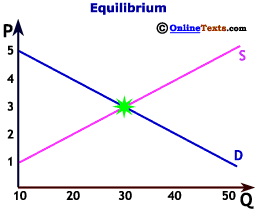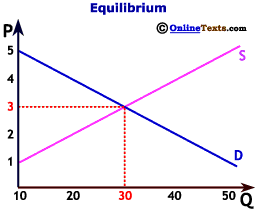
Before delving into the calculator, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of market equilibrium. In any market, the price of a good or service is determined by the interaction of supply and demand. The supply curve represents the quantity of a product that producers are willing to supply at various price levels, typically sloping upward as higher prices incentivize greater production. Conversely, the demand curve illustrates the quantity of a product that consumers are willing to purchase at different price points, generally sloping downward as higher prices reduce demand.
Equilibrium occurs at the price and quantity where the supply and demand curves intersect. At this point:
- Equilibrium Price (P*): The price at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
- Equilibrium Quantity (Q*): The quantity of the good or service bought and sold at the equilibrium price.
The Equilibrium Calculator: How It Works
An equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price calculator is a computational tool designed to find the intersection of the supply and demand functions. Users input the equations for both supply and demand, and the calculator solves for the equilibrium price and quantity. The general steps involved are:
Input Supply and Demand Functions:
Users provide the mathematical expressions for the supply and demand curves. For example:- Supply: ( Q_s = a + bP )
- Demand: ( Q_d = c - dP )
Where ( Q_s ) and ( Q_d ) are the quantities supplied and demanded, ( P ) is the price, and ( a, b, c, d ) are constants.
- Supply: ( Q_s = a + bP )
Set Quantity Supplied Equal to Quantity Demanded:
At equilibrium, ( Q_s = Q_d ). This equation is solved to find the equilibrium price (( P* )).Calculate Equilibrium Quantity:
Substitute the equilibrium price back into either the supply or demand equation to find ( Q* ).
Example Calculation
Consider the following supply and demand functions:
- Supply: ( Q_s = 10 + 2P )
- Demand: ( Q_d = 50 - P )
Set ( Q_s = Q_d ):
( 10 + 2P = 50 - P )Solve for ( P* ):
( 3P = 40 ) → ( P* = \frac{40}{3} \approx 13.33 )Find ( Q* ):
Substitute ( P* ) into the demand equation:
( Q* = 50 - 13.33 = 36.67 )
Thus, the equilibrium price is approximately $13.33, and the equilibrium quantity is approximately 36.67 units.
Step-by-Step Process for Using the Calculator
- Define the Functions: Write down the supply and demand equations.
- Set Equations Equal: Equate the quantity supplied to the quantity demanded.
- Solve for Price: Algebraically solve for the equilibrium price.
- Calculate Quantity: Use the equilibrium price to find the equilibrium quantity.
Applications of the Equilibrium Calculator
The equilibrium calculator is a versatile tool with applications across various fields:
- Policy Analysis: Governments use it to predict the impact of taxes, subsidies, or regulations on market prices and quantities.
- Business Strategy: Firms analyze how changes in production costs or consumer preferences affect equilibrium outcomes.
- Academic Research: Economists employ the tool to model market behavior and test economic theories.
"The equilibrium calculator is not just a theoretical tool; it’s a practical instrument for understanding real-world market dynamics. By quantifying the interplay of supply and demand, it empowers decision-makers to anticipate changes and formulate effective strategies." – Dr. Emily Carter, Economist
Limitations and Considerations
While the equilibrium calculator is powerful, it has limitations:
- Static Analysis: It assumes constant supply and demand functions, ignoring dynamic factors like technological advancements or shifts in consumer behavior.
- Ceteris Paribus Assumption: It relies on the “all else equal” assumption, which may not hold in complex, real-world markets.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of results depends on the correctness of input data and the realism of the supply and demand functions.
Pros and Cons of the Equilibrium Calculator
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Provides precise equilibrium values | Assumes static market conditions |
| Useful for policy and business decisions | Relies on accurate input data |
| Simplifies complex market analysis | Ignores external factors like market power |
Technological Advancements in Equilibrium Calculation
Modern technology has enhanced the functionality of equilibrium calculators. Software tools and online platforms now offer user-friendly interfaces, allowing even non-experts to perform complex calculations. For instance:
- Graphical Representation: Tools like Excel, Python, or specialized economics software can plot supply and demand curves and visually identify the equilibrium point.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Advanced calculators enable users to test how changes in parameters (e.g., slope of the curves) affect equilibrium outcomes.
- Dynamic Modeling: Some tools incorporate dynamic elements, such as time lags or feedback loops, to simulate real-world market behavior.
FAQ Section
What is market equilibrium?
+Market equilibrium is the point where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, resulting in a stable price and quantity.
How do I find the equilibrium price algebraically?
+Set the supply equation equal to the demand equation and solve for the price ( P* ).
Can the equilibrium calculator handle non-linear functions?
+Yes, advanced calculators can solve for equilibrium in non-linear supply and demand models, though it may require numerical methods.
What happens if supply and demand curves never intersect?
+If the curves never intersect, there is no equilibrium in the classical sense, indicating a market failure or external intervention.
How does elasticity affect equilibrium?
+Elasticity measures how responsive supply and demand are to price changes. Higher elasticity leads to larger shifts in equilibrium quantity relative to price changes.
Conclusion
The equilibrium quantity and equilibrium price calculator is an indispensable tool for economists, policymakers, and businesses seeking to understand and predict market behavior. By identifying the point where supply and demand intersect, it provides critical insights into pricing, production, and consumption patterns. While the calculator has limitations, its applications in both theoretical and practical contexts underscore its importance in economic analysis. As technology advances, these tools will continue to evolve, offering even greater precision and utility in deciphering the complexities of market dynamics.
Key Takeaway: The equilibrium calculator simplifies the analysis of market interactions, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on the principles of supply and demand. Its effectiveness lies in its ability to distill complex economic relationships into actionable insights.